
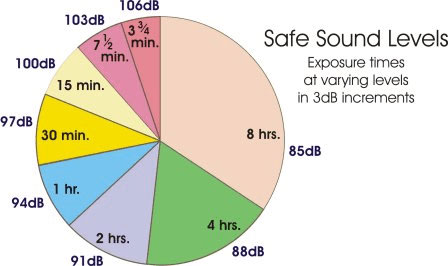
95 decibels: Just 10 minutes a day at this level can cause temporary hearing loss.The weekly limit at this level is 4 hours. 90 decibels: Around 30 minutes a day at this level can cause temporary hearing loss.The weekly limit at this level is around 12 hours and 30 minutes. 85 decibels: Around 1 hour and 45 minutes a day at this level can cause temporary hearing loss.
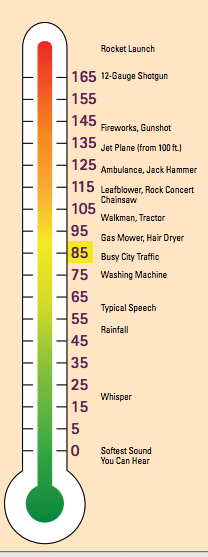
The weekly limit at this level is 40 hours. 80 decibels: Around 5 hours and 30 minutes a day at this level can cause temporary hearing loss.Sounds measured at this level appear as Loud in the app. Consider using hearing protection or moving to a quieter area. Repeated, long-term exposure to sounds above 80 decibels can lead to permanent damage.Sounds measured at this level appear as OK in the app.
 Long-term exposure to sounds below 80 decibels should not affect your hearing. Sound levels are measured in A-weighted decibels. Due to its effect on employees, it should be minimized where possible and should be managed at a local level. The cause of nuisance noise are wide ranging and can be quite difficult to control. However, this noise can have a psychological effect, cause stress, and impact employee performance. Noise levels below 85 dBA are not likely to damage hearing. ^ Back to Top What if noise is irritating but below exposure limits? Start by speaking to your supervisor to determine what is possible to implement in your workplace.Īll workers who are exposed to noise that exceeds exposure limits (85 dBA daily or 140 dBC peak sound level) must receive a hearing test no later than 6 months after starting work and annually thereafter. Hearing protection devices such as earplugs or earmuffs. Shift work hours, work at a distance, exposure control plans Use equipment designed to minimize noise, maintain/lubricate moving parts, use isolation booths/barriers ^ Back to Top How can I reduce noise hazards?Īs with any exposure, start by using the hierarchy of controls. This assessment will determine if a hearing test is required and if other controls need to be used in that area. If you are concerned that noise in your workplace exceeds 85 dBA, contact the Occupational Hygienist to arrange an on-site noise assessment. To obtain accurate results, workplace noise is often measured using a noise dosimeter or sound level meter.
Long-term exposure to sounds below 80 decibels should not affect your hearing. Sound levels are measured in A-weighted decibels. Due to its effect on employees, it should be minimized where possible and should be managed at a local level. The cause of nuisance noise are wide ranging and can be quite difficult to control. However, this noise can have a psychological effect, cause stress, and impact employee performance. Noise levels below 85 dBA are not likely to damage hearing. ^ Back to Top What if noise is irritating but below exposure limits? Start by speaking to your supervisor to determine what is possible to implement in your workplace.Īll workers who are exposed to noise that exceeds exposure limits (85 dBA daily or 140 dBC peak sound level) must receive a hearing test no later than 6 months after starting work and annually thereafter. Hearing protection devices such as earplugs or earmuffs. Shift work hours, work at a distance, exposure control plans Use equipment designed to minimize noise, maintain/lubricate moving parts, use isolation booths/barriers ^ Back to Top How can I reduce noise hazards?Īs with any exposure, start by using the hierarchy of controls. This assessment will determine if a hearing test is required and if other controls need to be used in that area. If you are concerned that noise in your workplace exceeds 85 dBA, contact the Occupational Hygienist to arrange an on-site noise assessment. To obtain accurate results, workplace noise is often measured using a noise dosimeter or sound level meter. DANGEROUS DECIBEL LEVELS DOWNLOAD
You can download an application on your smartphone, however the microphone in your device is likely not able to accurately detect higher intensity sounds. ^ Back to Top How can I measure noise levels in my workplace? 140 dBC sounds like a military aircraft with afterburners on. TO provide some perspective, 85 dBA sounds like a kitchen blender operating on high. 140 dBC peak sound level (maximum intensity on a C-weighted filter).85 dBA daily noise exposure level (A-weighted filter, averaged over an 8 hour period).OHSR 7.2 sets the following exposure limits:
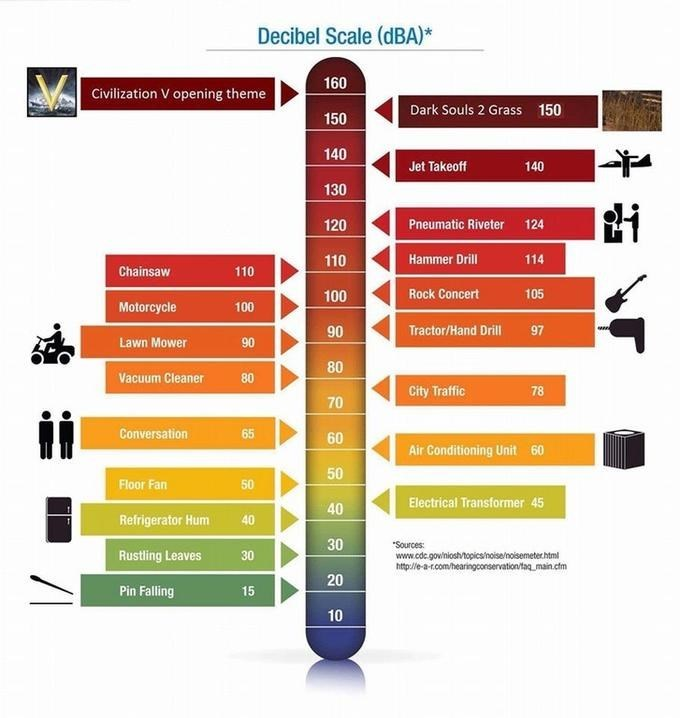
WorkSafeBC has strict limits for the intensity of sound permissible in the workplace. Duration: The length of time you have been exposed to noise.
Sound level meters account for this by using an “A” weighted filter
Frequency: Frequencies between 3000-4000 Hz are most likely to damage human hearing. Intensity/Loudness: This factor is measured by a noise level meter and the units are described in decibels (dB). The higher the dose of noise a worker receives the greater the risk to the workers hearing.Ī workers noise dose is dependent on the following 3 factors: ^ Back to Top How do I know if noise levels in my workplace are safe? When it comes to the workplace, noise is sound that is intense enough to cause hearing damage. However, if the vibrations are too strong, or they last for an extended period, the hairs can be permanently damaged causing hearing loss. The hairs can easily deform and return to their original position. Bending those hairs creates nerve impulses that the brain perceives as sound. These parts amplify the vibrations and ultimately cause tiny hairs in the inner ear to bend. When air molecules surrounding our wars vibrate, parts inside the ear can sense the changes in pressure. What if noise is irritating but below exposure limits? Noise Hazards What is noise? How can I measure noise levels in my workplace? How do I know if noise levels in my workplace are safe?








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
